The dispute between AI agent vs. generative AI This marks a new era in Artificial Intelligence. While previously the focus was on GenAI and its creative capabilities, today the emphasis is on autonomy and operational efficiency in business environments.
The confusion, however, persists: many startups leaders and product managers still treat AI Agent and Generative AI as synonyms or competing technologies.
For those seeking not only to optimize processes, but also reshaping entire business ecosystems, It is crucial to master the fundamental distinction in the clash. AI agent vs. generative AI.
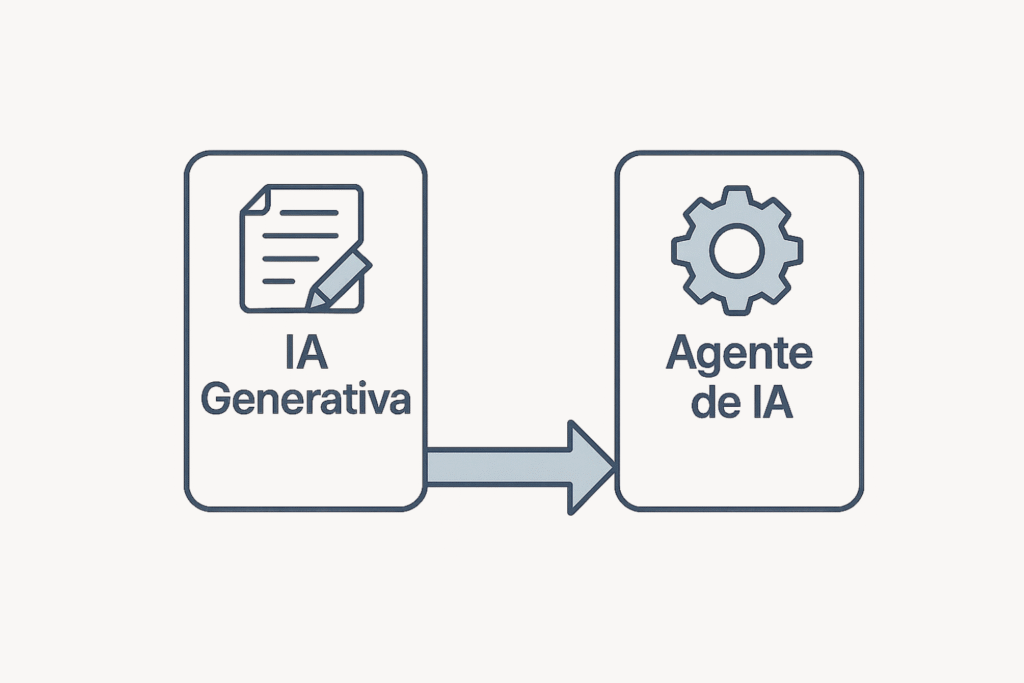
The central thesis is unequivocal and strategic: Generative AI, while revolutionary for its ability to reactively produce text, code, or images, is a fundamental tool in itself. prompt Simply put, it is, in fact, a critical component who resides within of the architecture of an AI Agent.
Generative AI (GenAI): The Cognitive Engine of Creation

For entrepreneurs or CTOs, generative AI should be seen as the creation tool.
Its primary function is to Transforming input data into new and coherent output content., based on patterns it has learned from vast datasets (Details about GenAI can be found in IBM and AWS).
The success of models like GPT, LaMDA, or Bard lies precisely in their ability to generate solutions, whether by writing a persuasive email, drafting code, or creating a conceptual image from a textual description.
This generation capability has profoundly impacted the job market, optimizing creative and repetitive tasks on a large scale (Check out the...). Impact of AI on the Global Job Market).
Definition and Classic Use Cases
GenAI essentially operates in a mode reactive. She is waiting for an instruction (the prompt), processes it internally and returns the result.
Its architecture is centered on the Large Language Model (LLM) or diffusion models (for images), its intrinsic value being... fluidity and the coherence of production.
In a business context, use cases are mostly of digital asset production:
- Content Creation: Generating blog articles, social media posts, or copy for advertising, significantly accelerating the marketing cycle, as detailed by Content Marketing Institute on GenAI.
- Code Generation: Assistance in writing functions, language conversion or debugging, transforming the LLM into a development co-pilot.
- Analysis and Summarization: Processing lengthy legal documents or financial reports, summarizing the key points concisely.
The Myth of Autonomy: Limitations of GenAI
The biggest misconception is expecting Generative AI to be capable of... act Alone in the real world, a pure GenAI cannot, for example, conduct market research, analyze the results, decide on the best launch strategy, and execute the social media post, all in sequence.
It lacks four fundamental elements that define autonomy:
- Persistent and Contextual Memory: Generative models typically have a limited context window. They "forget" previous interactions unless explicitly fed with history.
- Access to External Tools: GenAI, on its own, cannot navigate the internet in a structured way, interact with third-party APIs (such as a CRM or a payment platform), or use a code editor outside of the environment of [the relevant platform/service]. prompt.
- Multi-Stage Planning: She is limited to responding to immediate task. If the goal is "to increase sales in 10% in the next quarter," GenAI needs to manually break down that goal into steps (research, analysis, creation, execution).
- Feedback Loop: It lacks an inherent mechanism to self-evaluate the outcome of its actions in the environment and subsequently correct the plan.
This is where understanding AI infrastructure becomes crucial, as it forms the basis for scaling the capabilities of core models.
To delve deeper into the technical basis that underpins these tools, we recommend reading about... What is AI infrastructure and why is it essential?.

Agent AI vs. Generative AI: Unveiling the Proactive Agent Architecture
The real disruption for the business world lies in AI Agency (or AI Agent), which represents a leap from creation for the action.
The Agent is, conceptually, a software system that perceives its environment through sensors, processes this perception, makes decisions, plans and executes actions through actuators (tools) (For a detailed definition, see the...) AWS's explanation of AI Agents.).
Agent-based AI vs. generative AI It's not a duel, but rather a symbiotic relationship.
While Generative AI is the muscle that performs the generation of complex content or reasoning, the AI Agent is the autonomous pilot that defines the route, monitors traffic, and adjusts the speed.
The Action Loop: Perception, Reasoning, Planning, and Action
The architecture of an AI Agent operates in a continuous cycle, known as the "Action Loop" or O-OODA (Observe, Orient, Decide, Act – Adapted for AI).
This cycle ensures autonomy and self-correction capabilities, elements that are lacking in pure GenAI:
- Perception (Observe): The agent collects data from the environment (emails, sales data in a CRM, API notifications, web search results).
- Reasoning (Orient & Decide): Using its LLM (an internal GenAI), the Agent processes the target and perceived data, generating a logical plan. This is where the generative engine comes in. translate The state of the world in a sequence of actions.
- Planning (Plan): The agent breaks down the complex goal into executable subtasks (Example: "To achieve X, I first need to do A, then B, and only then C").
- Action (Act): The agent uses external tools (APIs, browsers, databases) to execute the plan in the real world.
- Adaptation (Feedback Loop): The agent evaluates the outcome of the action and uses the feedback to refine the next Perception/Reasoning cycle, ensuring learning and self-correction.
The Key Components of an AI Agent (LLM, Memory, Tools)
To function, an AI Agent needs more than just a powerful LLM (GenAI). It requires a robust data structure and functionality (Source: Google Cloud Generative AI Glossary).
- Large Language Model (LLM): Acts as the brain of the system, responsible for reasoning, planning, and generating the language that guides actions and interactions. It is the generative motor. The constant evolution of these models (such as the Grok, Gemini or ClaudeThis is what drives the Agents' power.
- Memory (Buffer/Persistent): It stores the history of the interaction (short and long term) and the state of the world that the agent perceived. This prevents repetition and ensures the continuity of planning.
- Tools/Plugins: These are the interfaces to the outside world. They can be APIs, specific code functions, or the ability to interact with No-Code platforms to, for example, update a table in a database or send a notification via Slack. Frameworks such as LangChain and CrewAI They are crucial to this orchestration.
Strategic Integration: Why GenAI is Essential for the Agent
The main difference between AI agent vs. generative AI It's not technological, but architectural and functional. GenAI is the engine. The Agent is the complete orchestra that uses that engine.
LLM, with its generative capabilities, is what transforms the AI Agent into an intelligent system, and not just an automaton based on rigid rules.
The power of the LLM lies in its ability to reasoning in natural language.
LLM as the 'Brain' of Reasoning (Plan Generation Mechanism)
When an AI Agent receives a goal (example: “Find 5 leads in the sector of Fintech in São Paulo and generate a contact report”), the internal LLM is called in for the reasoning phase.
He not only creates a text, but Create the action plan. which leads to the goal, using language as its means of calculation.
The LLM thinks:
- I need the 'Web Search' tool to find contact information for Fintech companies in São Paulo.
- I need the 'Data Validator' tool to filter out valid emails.
- I need the 'Report Generator' tool (also GenAI) to format the final report.
It is generative capacity to produce this logical and operational chain that differentiates the AI Agent from a chatbot common or simple workflow automation. Studies on Agent-Based Reasoning on ResearchGate They demonstrate this power.
The complexity of reasoning in generative AI is a field of intense academic study (Read more at SciELO on the topic).
No-Code Automation with AI Agents: From Theory to Practice
For the No Code Startup community, the adoption of AI Agents is a game-changer. Traditionally, No-Code/Low-Code simplified the creating interfaces and flows.
With Agency AI, the focus shifts to creating autonomous intelligence which uses these flows intelligently.
Consider a Customer Service Agent. They not only generate responses (GenAI's task), but also:
- Understand The customer's message (via the chat API).
- Think Regarding intent (LLM).
- Plan the action (Ex.: If it is bug, Create a ticket in Trello; if it is sale, (send payment link).
- Action (Interacts with Trello API and Stripe API).
This level of autonomy, built upon the foundation of AI agent vs. generative AI (Understanding GenAI as an engine), it allows startups to develop complex functionalities without writing hundreds of lines of code.
It is the union of AI Coding Training: Create Apps with AI and Low-Code with the power of agentic frameworks, allowing the construction to be focused on business logic and not on syntax.

The Future: Real-World Use Cases and the Market Shift
The market trend is clear: Agency AI will be the main driver of exponential growth in the coming years, moving the market value of... tools creation for systems execution.
The difference between AI agent vs. generative AI It's the difference between having a powerful engine and having a self-driving car.
Applied Examples in Startups
The value of AI agents becomes apparent in contexts where task complexity and the need for interaction with the real world are high:
- Proactive Data Analyst: Instead of just responding to one prompt Regarding the data (“What was the profit last month?”), a proactive AI Agent has the goal of “Optimizing Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)”.
It can monitor ad spending in real time and automatically analyze the... funnels conversion tracking, detecting anomalies (using LLM for reasoning), and autonomously pausing low-performing campaigns via the ad platform's API. - Independent Sales Agent: An agent who receives a list of leads, uses GenAI to customize the pitch The contact system sends the email via a No-Code system, monitors the open rate, and, if there is interest, automatically schedules a meeting in the salesperson's calendar, updating the status in the CRM.
For more details on the application in sales, see the Gartner's analysis of Autonomous Selling with AI. - Content Sourcing Agent: The agent monitors industry news, uses GenAI to summarize the content and rank it by relevance, and then autonomously publishes a summary in the internal community or on the blog (after human review), keeping the ecosystem always up-to-date.
How to Start Building Agents with Low-Code/No-Code
Adopting AI Agents doesn't require a team of PhDs in Machine Learning. The synergy between Low-Code/No-Code and LLM APIs (the generative engine) makes building agents accessible.
Modern No-Code platforms already offer connectors and tools to create the loop of perception and action:
- Define the Goal (and the KPI): Start with a clear and measurable goal (e.g., Reduce the average support response time in 20%).
- Identify the Tools: Map out the systems that the Agent needs to use (email, Slack, database, Trello).
The integration of AI with Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is an accelerating factor (See The role of RPA in the era of Agency AI.). - Use LLM as a Reasoner: Configure LLM (GenAI) to translate the world state and the goal into a flat logical way of using the tools.
The focus should be on rapid and iterative implementation, a central characteristic of the No-Code Startup philosophy.
Strategic Implementation for Startups: The No Code Startup Path
The decision to invest in an AI Agent is fundamentally a strategic decision regarding the allocation of time and resources.
For the No Code Startup, the question agent of pathway or generative pathway It is crucial for optimizing business processes with AI.
GenAI optimizes production. The AI Agent optimizes the value stream complete.
Agent Adoption and Process Optimization
The successful implementation of Agency AI begins with identifying process bottlenecks that are too complex for simple rule-based automations (If This, Then That), but they still consume human time.
The crucial difference of an AI Agent is that it can adapt to unforeseen scenarios within an overall goal.
For example, in the Human Resources sector, an Agent can:
- Analyze resumes (GenAI).
- Compare with the job description (LLM reasoning).
- Schedule interviews (Action via Calendar API).
- Send technical tests (Action via testing platform).
- And if the candidate does not respond, send a reminder (Adaptation based on feedback loop).
No Code Start Up offers robust solutions for companies seeking this level of proactive automation, through AI and Automation Agents: No-Code Solution for Businesses.
Challenges and Governance of Agency AI
Despite its potential, Agency AI presents unique challenges, primarily related to control and security.
Autonomy means that the agent can, on rare occasions, generate unintentional actions ("action hallucinations").
Governance should focus on:
- Sandboxing: Limit the scope of tools that the Agent can access and use.
- Human Supervision: Ensure that the Agent requests "permission" for high-risk actions (e.g., making a financial transaction or sending mass communications to clients).
- Transparency of Reasoning: The agent must be able to explain the why of their actions (the chain of thought (generated by the LLM), facilitating auditing and correction. The ethical debate surrounding AI autonomy is central (Read about Ethics in Autonomous AI Systems).
Agency AI is a journey, not a destination. Its implementation should be phased, starting with low-risk processes and gradually expanding as trust in the system and maturity increase. agency AI architecture They increase.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What does Agency AI mean?
Agency AI refers to Artificial Intelligence systems that have the ability to perceive an environment, make autonomous decisions, plan a sequence of actions, and execute them in the real world (usually via APIs and tools).
Unlike reactive generative AI, the AI Agent is proactive and works continuously towards a long-term goal, adapting its plan based on the results of its actions.
Will Generative AI be replaced by AI Agents?
No. Generative AI will not be replaced, as it is a essential component The AI Agent. GenAI, specifically the LLMs, acts as the Agent's reasoning and communication engine, being responsible for interpreting data, creating action plans, and generating the interface text or code necessary for the tasks.
GenAI is the cognitive engine; the AI Agent is the autonomous execution system.
What are the main practical differences in usage between the two AIs?
The practical difference is that GenAI requires a prompt for each step and cannot interact with external systems without manual intervention.
The AI Agent can be given a high-level goal (e.g., "Monitor Twitter and notify me of brand crises"), and it will autonomously execute all the steps: research, analysis, classification (using GenAI), and notification (using external tools).
GenAI is a creation tool, while the AI Agent is a autonomous automation system. For further information, see the Practical difference between GenAI and Agents
Where can I build an AI agent without needing complex code?
You can build proactive AI systems using Low-Code and No-Code platforms that offer direct integrations with LLM APIs (OpenAI, Google, Anthropic) and connectors for business tools (CRM, ERP, databases).
These platforms allow you to visually map the loop of Perception, Reasoning (GenAI) and Action, focusing on business logic, not programming complexity. The era of simple content generation is ending, giving way to the era of... autonomous execution.
Understanding the hierarchy AI agent vs. generative AI It is the compass for any leader who wants to build a product or optimize an operation in a scalable way.
Generative AI is incredibly powerful, but it's only half the equation; it needs the agentic architecture to interact, adapt, and, fundamentally, deliver value continuously in the complex environment of a business.
The future doesn't belong to those who only know how to generate content, but rather to those who know how to build intelligent systems that... act for the business.
To take the next step and transform this architecture into real, scalable, and functional products, we invite you to explore the... AI Coding Training From No Code Startup, master the art of creating AI solutions without code. who think and act.