Discover the fascinating world of AI agents in this comprehensive guide! Learn from the basics of artificial intelligence to creating AI applications without the need for coding.
Table of Contents
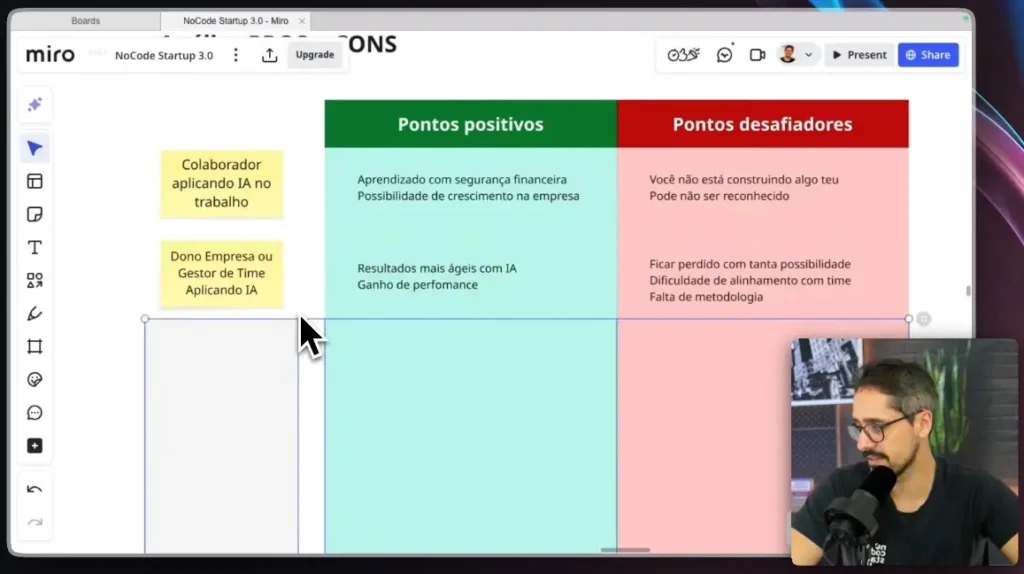
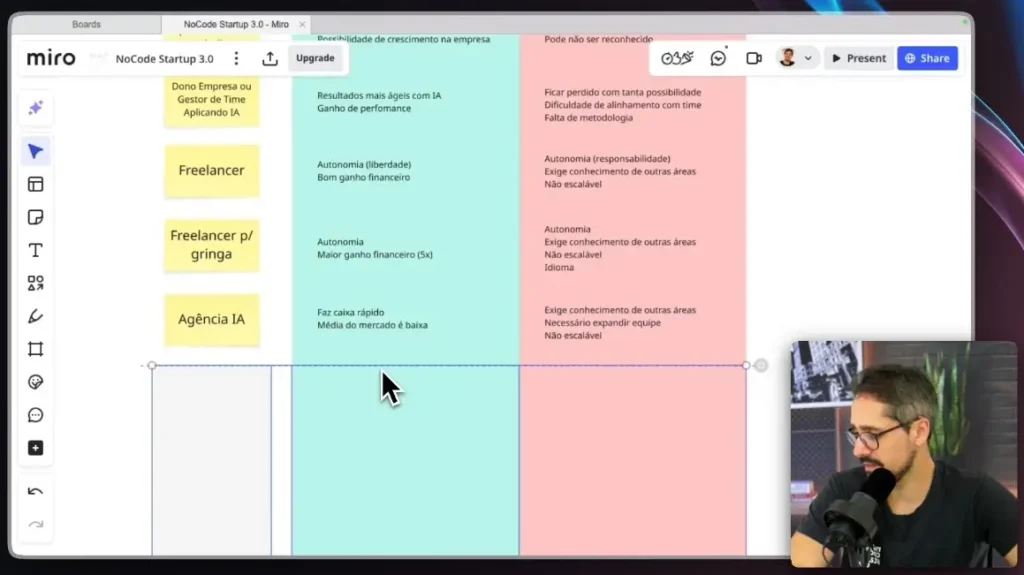
What are the different categories of AI?
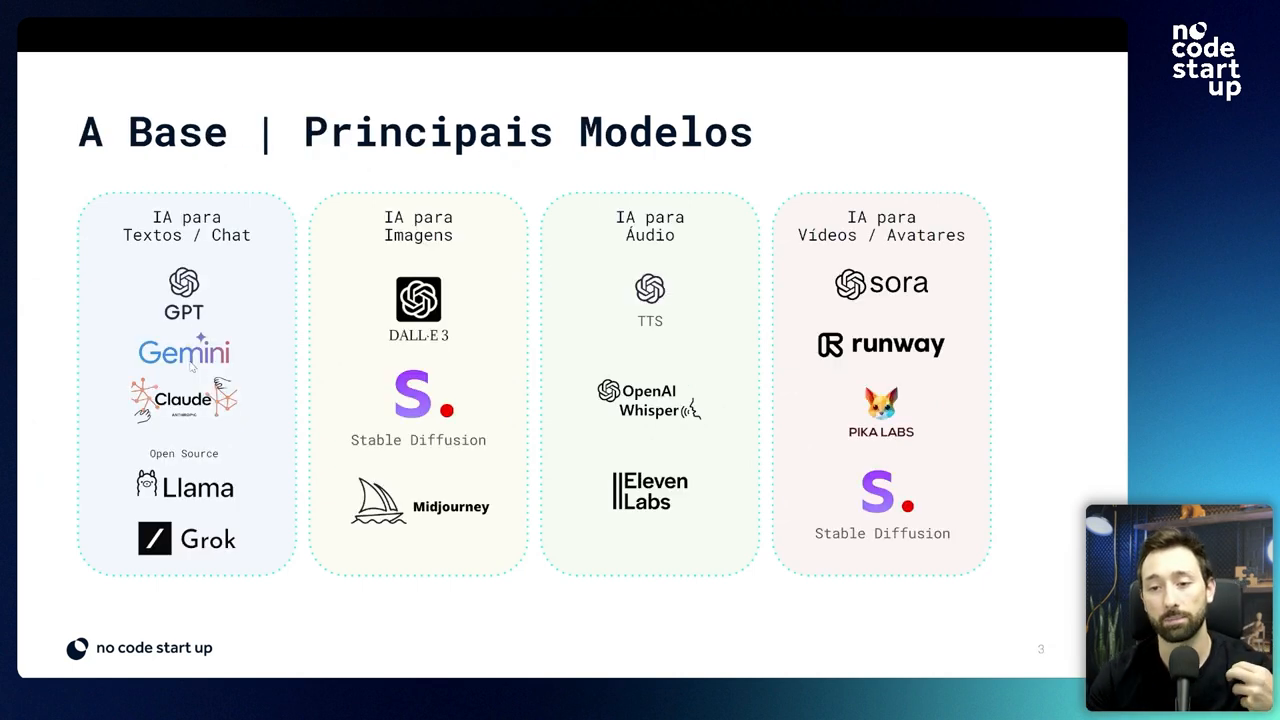
Artificial Intelligence (AI) categories vary and cover a wide range of applications. Let's explore the main categories of AI.
AI for Text
Firstly, text AI models are designed to understand, generate and manipulate text. They are widely used in chatbots, virtual assistants and translation tools. Some notable examples include:
- OpenAI's GPT-4
- Gemini by Google
- Claude by Anthropic
- LLaMA from Facebook
- Twitter Grok
AI for Images
Additionally, AI models for images are used for image recognition, generation, and editing. They have applications in areas such as medical diagnosis, security and digital art. Highlighted examples are:
- DALL-E by OpenAI
- Stable Diffusion
- MidJourney
AI for Audio
Audio AI models are used for speech recognition, speech synthesis, and audio analysis. They are essential in voice assistants and automatic transcription. Examples include:
- OpenAI Whisper
- 11 Labs models
AI for Video
Finally, AI models for video are applied in object recognition, motion analysis, and video generation. They are used in surveillance, entertainment and social media. Examples are:
- Runway
- Stable Diffusion
- PickLabs
What is an AI agent?
An AI agent is a central concept in the field of artificial intelligence. Let's better understand what defines an AI agent.
AI Agent Definition
According to Amazon's definition, an AI agent is a software program that can interact with its environment, collect data, and use that data to perform tasks and achieve predetermined goals.
Autonomy and Objectives
Furthermore, AI agents are designed to act independently. They receive input from the user and choose the best actions to achieve the established goal.
Travel Agent Analogy
A good analogy to understand an AI agent is to compare it to a travel agent. The travel agent collects various information to create an ideal travel plan for the client. Similarly, an AI agent uses various tools and data to achieve its goal.
What is the architecture of an AI agent?
The architecture of an AI agent is made up of several essential components. Let's explore these components in detail.
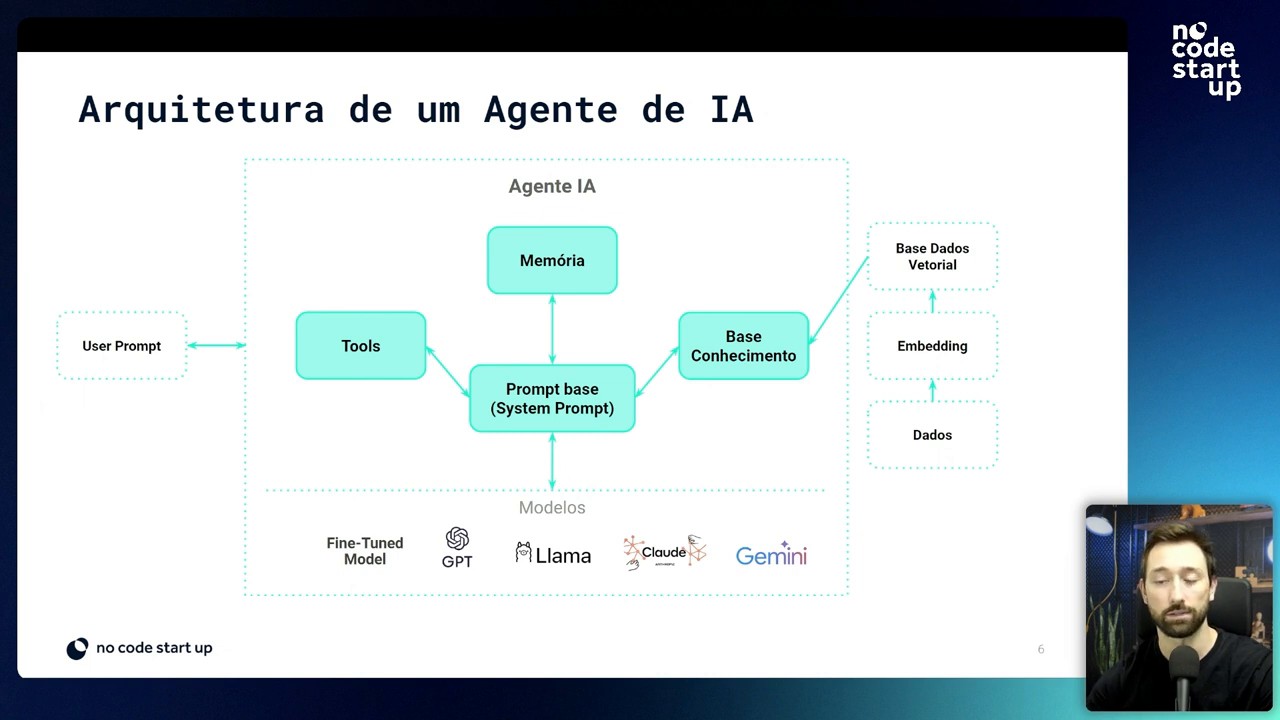
AI Models
AI agents rely on robust AI models like GPT, LLaMA, Claude, and Gemini. These models provide the necessary knowledge base for the agent.
Pre-Trained Models
Pre-trained, or “fine-tuned”, models are tuned with specific data to improve the agent’s performance on specific tasks.
Base Prompt
The base prompt is a set of instructions that define the agent's rules and personality. It guides the agent on what it can or cannot do.
Long Term Memory
Long-term memory allows the agent to maintain the context of previous conversations, making it more efficient and intelligent.
Extra Knowledge Bases
Extra knowledge bases include specific documents, spreadsheets, and other data that the agent can query to provide more accurate answers.
- PDF files
- Excel Spreadsheets
- Books
Indexing Process
The indexing process transforms data into vectors that are stored in vector databases. This allows the agent to search for information efficiently.
Tools and Functions
The tools and functions available to AI agents allow them to perform specific tasks, such as accessing the internet or making API calls.
- Code reading
- Internet access
- API calls
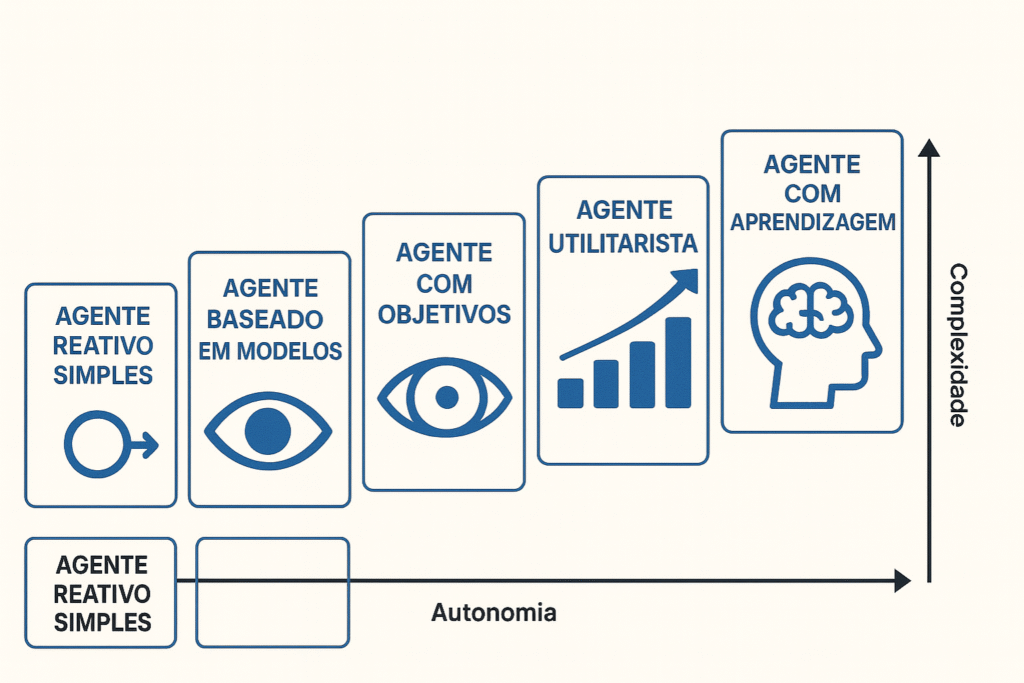
What are the different levels of AI agents?
AI agents can be classified into different levels, ranging from simple to advanced.
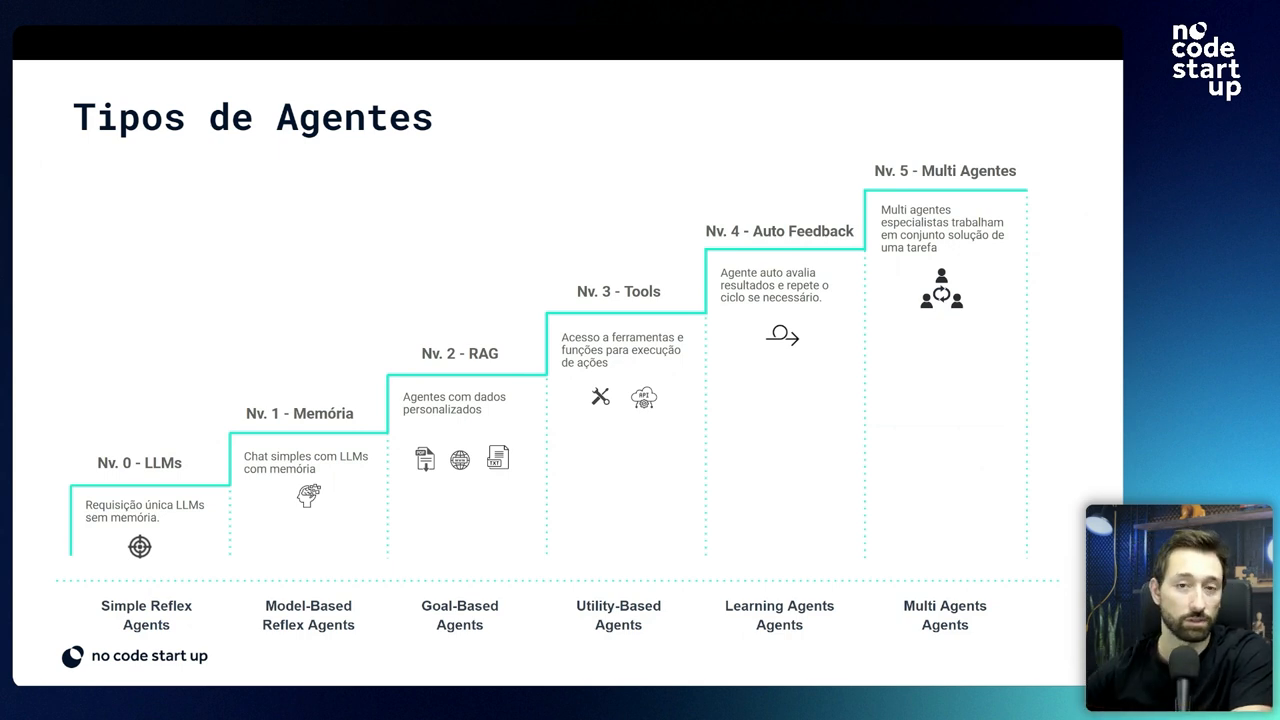
Level 0: Simple Reflex Agents
At the most basic level, we have Simple Reflex Agents. These agents react to immediate stimuli without memory or context.
- Single application for LLM
- Quick and unique responses
- No context or memory
Level 1: Model-Based Reflex Agents
The next level includes agents that have basic memory, allowing for simple, context-limited conversations.
- Simple chat with LLM
- Short-term memory
- Limited context
Level 2: Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
At level two, agents can access extra knowledge bases to provide more informed responses.
- Search in databases
- Information from PDFs, Excel, etc.
- Specific objectives
Level 3: Utility-Based Agents
These agents have the ability to perform more complex actions, such as API calls, integrating with other systems.
- Executing actions via API
- Integration with CRM and other systems
- Structured Functions
Level 4: Learning Agents
Level four agents can self-evaluate their results and repeat cycles to improve the quality of responses.
- Self-assessment of results
- Repeating cycles to improve
- Internal feedback
Level 5: Multi-Agents
The most advanced level includes multiple agents collaborating to achieve a common goal efficiently.
- Collaboration between agents
- Auto feedback between agents
- Common goal
What is the current scenario for AI agents?
The current landscape of AI agents is rapidly evolving, with continuous advancements and new applications emerging.
Tool Development
There are several tools being developed to facilitate the creation of AI agents at different levels.
- no-code Tools
- Development platforms
- Specialized APIs
Diversified Applications
AI agents are being applied in diverse areas, from customer service to business process automation.
- Customer service
- Process automation
- Technical support
Rapid Evolution
We are just at the beginning of the journey of developing AI agents, with significant disruptive potential.
- Beginning of construction
- Accelerated evolution
- Disruptive potential
What is the difference between an AI agent and a traditional chatbot?
Understanding the difference between an AI agent and a traditional chatbot is crucial to choosing the right solution for your needs.

AI Agents
AI agents use generative artificial intelligence and natural language processing to interact in a more human and efficient way.
- Generative artificial intelligence
- Natural Language Processing
- Context-based responses
Traditional Chatbots
Traditional chatbots follow a pre-defined, often rigid, conversational flow based on code scripts or manually constructed blocks.
- Predefined conversation flows
- Code Scripts
- Limited interaction
Mix of Technologies
There is a growing trend to integrate traditional chatbots with AI technologies to create more robust and adaptable solutions.
- AI integration in chatbots
- Knowledge base queries
- More accurate and informed responses
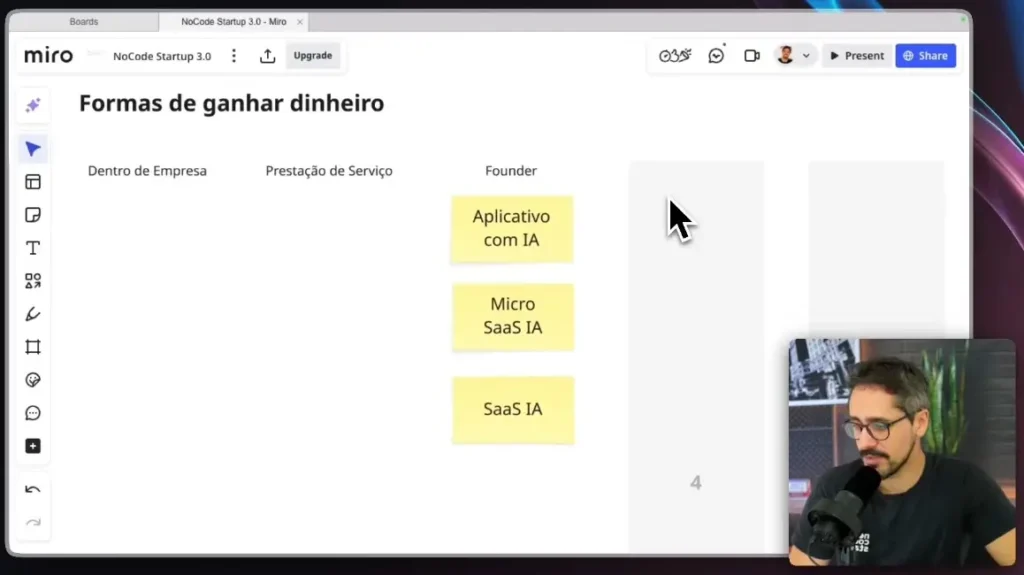
How to use AI agents in no-code applications?

AI agents are powerful tools that can be integrated into no-code applications to automate processes and improve efficiency.
Integration via API
The integration of AI agents into platforms no-code is often accomplished through API calls. This allows communication between different systems and AI.
With APIs, it is possible to connect AI agents to various tools and platforms, such as WhatsApp, Instagram, and custom systems created on the FlutterFlow or Bubble.
Integration Tools
Integration tools like Make and N2N make it easy to connect AI agents and other applications. They allow users to configure workflows without having to write code.
- make up
- N2N
- Zapier
Practical Applications
AI agents can be integrated into a variety of applications, from social media chatbots to business automation systems.
- Chatbots on WhatsApp
- Marketing automation
- Customer service systems