Artificial intelligence has advanced rapidly and AI agents are at the heart of this transformation. Unlike simple algorithms or traditional chatbots, intelligent agents are able to perceive the environment, process information based on defined objectives and act autonomously, connecting data, logic and action.
This advancement has driven profound changes in the way we interact with digital systems and carry out everyday tasks.
From automating routine processes to supporting strategic decisions, AI agents have been playing fundamental roles in the digital transformation of companies, careers and digital products.
What is an AI agent?
For an even more practical introduction, check out the AI Agent and Automation Manager Training from NoCode StartUp, which teaches step by step how to structure, deploy and optimize autonomous agents connected with tools such as N8N, Make and GPT.
One AI agent is a software system that receives data from the environment, interprets this information according to previously defined objectives and executes actions autonomously to achieve these objectives.
It is designed to act intelligently, adapting to context, learning from past interactions, and connecting to different tools and platforms to perform different tasks.

How Generative AI Agents Work
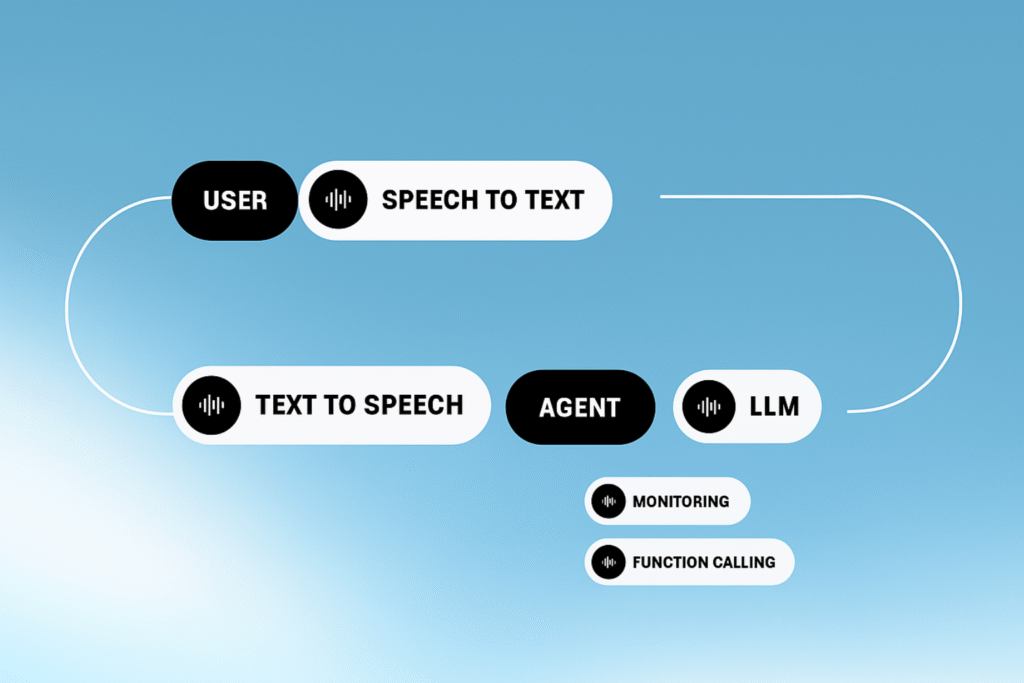
According to IBM, generative AI-based agents use advanced machine learning algorithms to generate contextualized responses and decisions — this makes them extremely efficient in personalized and dynamic flows.
Generative AI agents use large-scale language models (LLMs), such as those from OpenAI, to interpret natural language, maintain context between interactions, and produce complex, personalized responses.
This type of agent goes beyond simple reactive response, as it integrates historical data, decision rules and access to external APIs to perform tasks autonomously.
They operate on an architecture that combines natural language processing, contextual memory and logical reasoning engines.
This allows the agent to understand user intent, learn from previous feedback, and optimize its actions based on defined goals.
Therefore, they are ideal for applications that require deeper conversations, continuous personalization and autonomy for practical decisions.
Watch the free video from NoCode StartUp and understand from scratch how a conversational and automated AI agent works in practice:
Difference between chatbot with and without AI agent technology
While the terms “chatbot” and “AI agent” are often used interchangeably, there is a clear distinction between the two. The main difference lies in autonomy, decision-making capabilities, and integration with external data and systems.
While traditional chatbots follow fixed scripts and predefined responses, AI agents apply contextual intelligence, memory, and automated flows to perform real actions beyond conversation.
Traditional chatbot
A conventional chatbot operates on specific triggers, keywords, or simple question-and-answer flows. It usually relies on a static knowledge base and lacks the ability to adapt or customize continuously.
Its usefulness is limited to conducting basic dialogues, such as answering frequently asked questions or forwarding requests to human support.
Conversational AI Agent
An AI agent is built on a foundation of artificial intelligence capable of understanding the context of the conversation, retrieving previous memories, connecting to external APIs, and even making decisions based on conditional logic.
In addition to chatting, it can perform practical tasks — such as searching for information in documents, generating reports or triggering flows in platforms such as Slack, Make, N8N or CRMs.
This makes it ideal for enterprise applications, custom services, and scalable automations.
For an in-depth analysis of the concepts that differentiate rule-based automations and intelligent agents, it is also worth checking out the official MIT documentation on intelligent agents.
Comparison: AI agent, chatbot and traditional automation

To delve deeper into the theory behind these agents, concepts such as “rational agent” and “partially observable environments” are addressed in classic AI works, such as the book Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, by Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig.
Types of AI Agents
AI agents can be classified based on their complexity, degree of autonomy, and adaptability. Knowing these types is essential to choosing the best approach for each application and to implementing more efficient and context-appropriate solutions.
Simple reflex agents
These agents are the most basic, reacting to immediate stimuli from the environment based on predefined rules. They have no memory and do not evaluate the history of the interaction, which makes them useful only in situations with completely predictable conditions.
Example: a home automation system that turns on the light when it detects movement in the room, regardless of time or user preferences.
Model-based agents
Unlike simple reflex agents, these maintain an internal model of the environment and use short-term memory. This allows for more informed decisions, even when the scenario is not fully observable, as they consider the current state and recent history to act.
Example: a robot vacuum cleaner that recognizes obstacles, remembers areas already cleaned and adjusts its route to avoid repeating unnecessary tasks.
Goal-based agents
These agents work with clear goals and structure their actions to achieve these objectives. They evaluate different possibilities and plan the necessary steps based on desired results, which makes them ideal for more complex tasks.
Example: a logistics system that organizes deliveries based on the lowest cost, time and most efficient route, adapting to external changes, such as traffic or emergencies.
Utility-based agents
This type of agent goes beyond objectives: it evaluates which action will generate the greatest value or utility among several options. It is indicated when there are multiple possible paths and the ideal is the one that generates the greatest benefit considering different criteria.
Example: a content recommendation platform that evaluates user preferences, schedule, available time and context to recommend the most relevant content.
Learning agents
They are the most advanced and have the ability to learn from past experiences through machine learning algorithms. These agents adjust their logic based on previous interactions, becoming progressively more effective over time.
Example: a virtual customer service agent who, throughout conversations, improves their responses, adapts the tone and anticipates doubts based on the most frequently asked questions.
To understand how the use of AI is becoming a key factor in global digital transformation, McKinsey & Company published a detailed analysis on trends, use cases and economic impact of AI in business.

AI Agent Use Cases
Companies like OpenAI have been demonstrating in practice how agents based on LLMs are capable of executing complete workflows autonomously, especially when integrated with platforms such as Zapier, Slack or Google Workspace.
The application of artificial intelligence agents is rapidly expanding across various sectors and market niches.
With the evolution of no-code tools and platforms such as N8N, make up, Dify and Bubble, the creation of autonomous agents is no longer restricted to advanced developers and has become part of the reality of professionals, companies and creators of digital solutions.
These agents are especially effective when combined with automation tools, enabling complex workflows without the need for code. Below, we explore how different industries are already benefiting from these intelligent solutions.
Marketing and Sales
In the commercial sector, AI agents can automate everything from the first contact with leads to the generation of personalized proposals.
Through platforms like N8N, it is possible to create flows that collect data from forms, feed CRMs, send personalized emails and track the customer journey.
Additionally, these agents can analyze user behavior and adapt nurturing approaches based on previous interactions.
Service and Support
Companies that handle high volumes of interactions benefit from AI agents trained based on internal documents, FAQs, or databases.
With Dify and Make, for example, you can build assistants that answer questions in real time, automatically open tickets, and notify teams via Slack, email, or other integrations.
Education and Training
In the educational field, agents can be used to guide students, suggest content based on individual progress and even correct tasks in an automated way.
This automation illustrated below shows how AI agents can be practically implemented using N8N. In the flow, we have a financial agent personalized that converses with the user, accesses a Google Sheets spreadsheet to view or record expenses, and responds based on defined logic, allowed categories, and contextual validations.
The agent receives commands like “Show me my expenses for the week” or “Record an expense of R$120 on studies called 'Excel Course'”, and performs all actions automatically, without human intervention.

AI Agent FAQs
What can I automate with an AI agent?
AI agents are extremely versatile and can be used to automate everything from simple tasks — such as responding to emails and organizing information — to more complex processes such as reporting, customer service, lead qualification, and integration between different tools.
It all depends on how it is configured and what tools it accesses.
What is the difference between an AI agent and a customer service bot?
While a traditional bot answers questions based on keywords and fixed flows, an AI agent is trained to understand context, maintain memory, and make autonomous decisions based on logic and data. This allows it to take practical actions and go beyond conversation.
Do I need to know how to program to create an AI agent?
No. With no-code tools like N8N, Make, and Dify, you can create sophisticated agents using visual flows. These platforms allow you to connect APIs, build conditional logic, and integrate AI without having to write a line of code.
Is it possible to use AI agents with WhatsApp?
Yes. With platforms like Make or N8N, you can integrate AI agents into WhatsApp using third-party services like Twilio or Z-API. This way, the agent can interact with users, answer questions, send notifications, or capture data directly from the messaging app.
Why Learn to Build AI Agents Now

Mastering the creation of AI agents represents a competitive advantage for any professional who wants to stand out in the current market and prepare for the future of work.
By combining no-code tools with the power of artificial intelligence, it becomes possible to develop intelligent solutions that transform operational routines into automated and strategic flows.
These agents are applicable in different contexts, from simple tasks such as organizing emails, to more advanced processes such as generating reports, analyzing data or providing automated service with natural language.
And the best part: all of this can be done without relying on programmers, using accessible and flexible platforms.
Get started today with AI Agent Manager Training, or deepen your automation expertise with the N8N Course to create agents with greater integration and data structure and take the first step towards building more autonomous, productive and intelligent solutions for your routine or business.