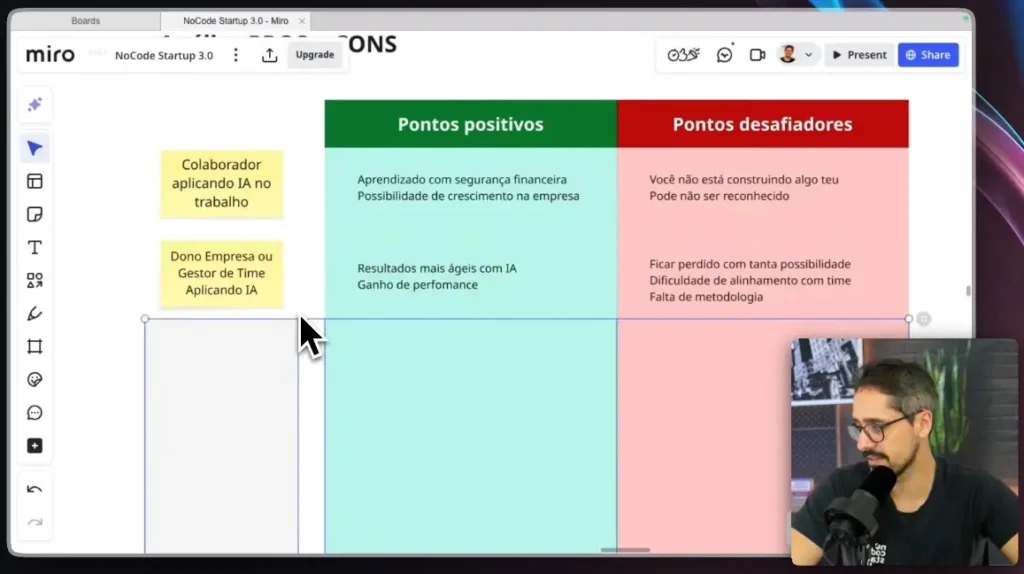
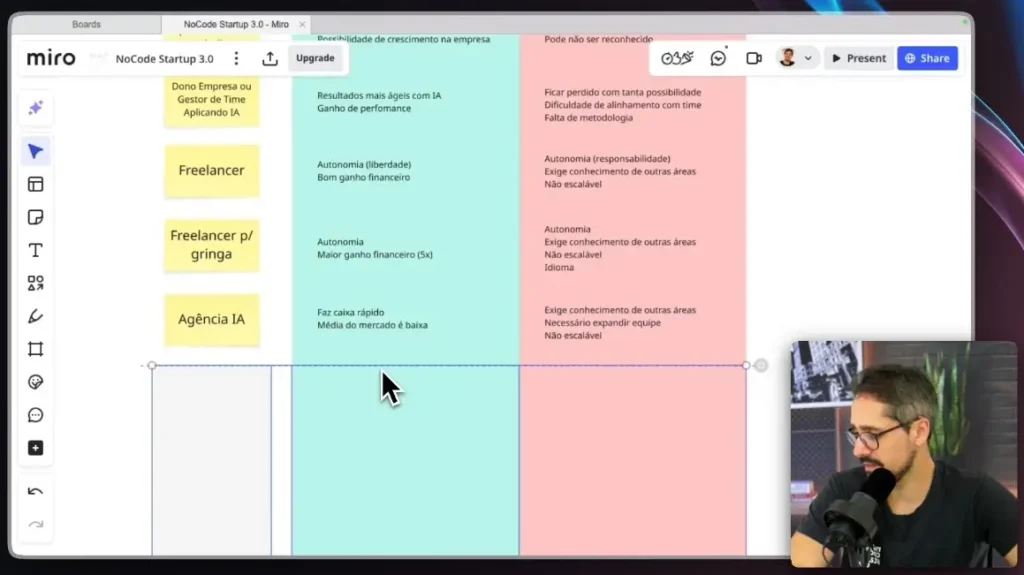
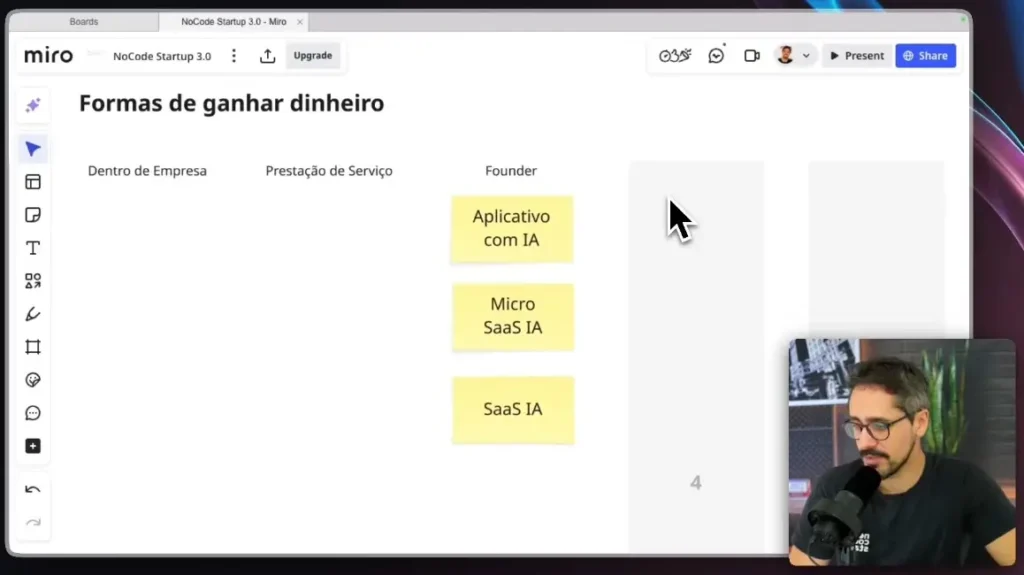
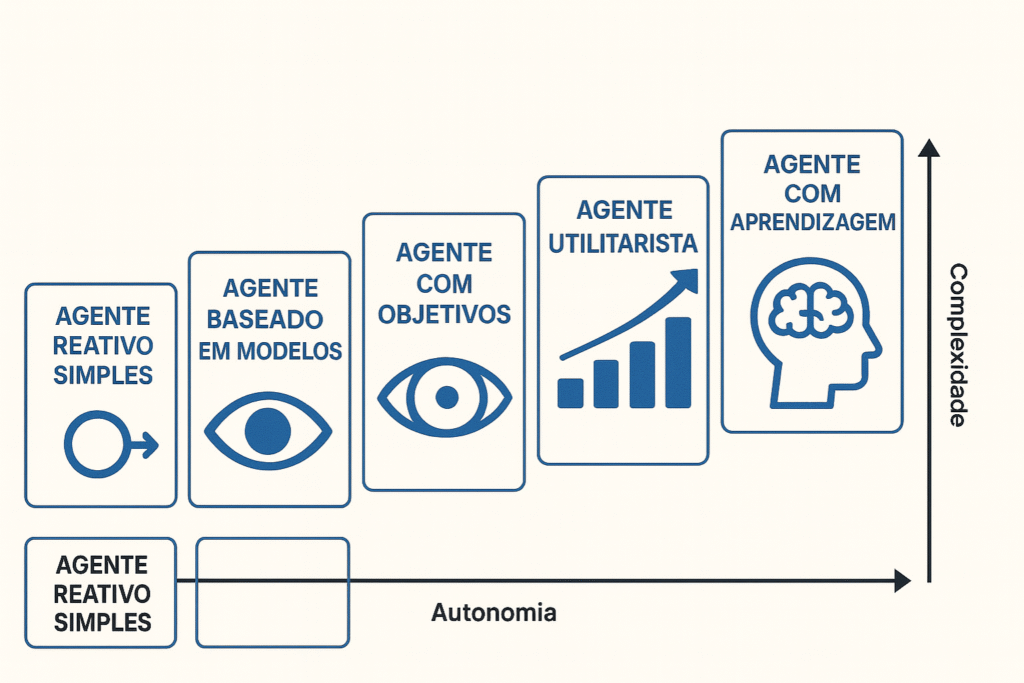
The evolution of artificial intelligence has reached significant milestones, and the arrival of multimodal AI This represents one of the most important transitions in this ecosystem.
In a world where we interact with text, images, audio, and video simultaneously, it makes sense that AI systems should also be able to understand and integrate these multiple forms of data.
This approach revolutionizes not only how machines process information, but also how they interact with humans and make decisions.
What is Multimodal AI?
Multimodal AI It is a branch of artificial intelligence designed to process, integrate, and interpret data from different modalities: text, image, audio, video, and sensory data.
Unlike traditional AI, which operates with a single source of information, multimodal models They combine various types of data for a deeper and more contextual analysis.
This type of AI seeks to replicate the way humans understand the world around them, since we rarely make decisions based on just one type of data.
For example, when watching a video, our interpretation takes into account both visual and auditory and contextual elements.
How does Multimodal AI work in practice?
The foundation of multimodal AI lies in data fusion. There are different techniques for integrating multiple sources of information, including early fusion, intermediate fusion, and late fusion.
Each of these approaches has specific applications depending on the context of the task.
Furthermore, multimodal models utilize intermodal alignment (or cross-modal alignment) to establish semantic relationships between different types of data.
This is essential to allow AI to understand, for example, that an image of a "dog running" corresponds to a text caption that describes that action.

Technical Challenges of Multimodal AI
Building multimodal models involves profound challenges in areas such as:
- RepresentationHow do you transform different data types—such as text, image, and audio—into comparable numerical vectors within the same multidimensional space?
This representation is what allows AI to understand and relate meanings between these modalities, using techniques such as embeddings and specific encoders for each data type. - AlignmentHow can we ensure that different modalities are semantically synchronized? This involves the precise mapping between, for example, an image and its textual description, allowing AI to accurately understand the relationship between visual elements and language.
Techniques such as cross-attention and contrastive learning are widely used. - Multimodal reasoningHow can a model infer conclusions based on multiple sources? This ability allows AI to combine complementary information (e.g., image + sound) to make smarter and more contextualized decisions, such as describing scenes or answering visual questions.
- GenerationHow to generate output in different formats coherently? Multimodal generation refers to creating content such as image captions, spoken responses to written commands, or explanatory videos generated from text, always maintaining semantic consistency.
- TransferHow can a model trained with multimodal data be adapted for specific tasks? Knowledge transfer allows a generic model to be applied to specific problems with minimal customization, reducing development time and data requirements.
- QuantificationHow can we measure performance using comparable criteria across different modalities? This requires metrics adapted to the multimodal nature of media, capable of evaluating consistency and accuracy between text, image, audio, or video in a unified and fair way.
Main Benefits of Multimodal Models
By integrating multiple sources of information, multimodal AI offers undeniable competitive advantages.
Firstly, it significantly increases the accuracy of decision-making, as it allows for a more complete understanding of the context.
Another strong point is robustness: models trained with multimodal data tend to be more resilient to noise or failures in one of the data sources.
Furthermore, the ability to perform more complex tasks, such as generating images from text (text-to-image), is driven by this type of approach.
How to Evaluate Multimodal Models?
To measure the quality of multimodal models, different metrics are applied depending on the task:
- BLEU multimodal: evaluates quality in text generation tasks with visual input.
- Recall@k (R@k): used in cross-modal searches to check if the correct item is among the top-k results.
- FID (Fréchet Inception Distance): used to measure the quality of images generated based on textual descriptions.
Accurate evaluation is essential for technical validation and comparison between different approaches.
Real-World Examples of Multimodal AI in Action
Several technology platforms already use multimodal AI on a large scale. The model Gemini, Google's [model name] is an example of a foundational multimodal model designed to integrate text, images, audio, and code.
Another example is GPT-4o, which accepts voice and image commands along with text, offering a highly natural user interaction experience.
These models are present in applications such as virtual assistants, medical diagnostic tools, and real-time video analysis.
To learn more about practical applications of AI, see our article on... Vertical AI Agents: Why this could change everything in the digital market.
Tools and Technologies Involved
The advancement of multimodal AI has been driven by platforms such as Google Vertex AI, OpenAI, Hugging Face Transformers, Meta AI and IBM Watson.
Furthermore, frameworks such as PyTorch and TensorFlow They offer support for multimodal models with specialized libraries.
Within the NoCode universe, tools such as Dify and make up They are already incorporating multimodal capabilities, allowing entrepreneurs and developers to create complex applications without traditional coding.

Multimodal Data Generation Strategies
The scarcity of well-matched data (e.g., text with image or audio) is a recurring obstacle. Modern techniques of data augmentation Multimodal options include:
- Using generative AI to synthesize new images or descriptions.
- Self-training and pseudo-labeling to reinforce patterns.
- Transfer between domains using multimodal foundational models.
These strategies improve performance and reduce biases.
Ethics, Privacy and Bias
Multimodal models, due to their complexity, increase the risks of algorithmic bias, abusive surveillance, and misuse of data. Best practices include:
- Continuous auditing with diverse teams (red-teaming).
- Adoption of frameworks such as EU AI Act and ISO AI standards.
- Transparency in datasets and data collection processes.
These precautions prevent negative impacts on a large scale.
Sustainability and Energy Consumption
Training multimodal models requires significant computational resources. Strategies to make the process more sustainable include:
- Quantization and distillation of models to reduce complexity.
- Use of renewable energy and optimized data centers.
- Tools like ML CO2 Impact and CodeCarbon for measuring carbon footprint.
These practices combine performance with environmental responsibility.
From Idea to Product: How to Implement
Whether with Vertex AI, watsonx, or Hugging Face, the process of adopting multimodal AI involves:
Stack choice: open-source or commercial?
The first strategic decision involves choosing between open-source tools or commercial platforms. Open-source solutions offer flexibility and control, making them ideal for technical teams.
Commercial solutions, such as Vertex AI and IBM Watson, accelerate development and provide robust support for companies seeking immediate productivity.
Data preparation and recording
This step is critical because the quality of the model depends directly on the quality of the data.
Preparing multimodal data means aligning images with text, audio with transcripts, videos with descriptions, and so on. Furthermore, the annotation must be accurate to train the model with the correct context.
Training and fine-tuning
With the data ready, it's time to train the multimodal model. This phase may include the use of foundational models, such as Gemini or GPT-40, which will be adapted to the project context via fine-tuning techniques.
The goal is to improve performance in specific tasks without having to train from scratch.
Implementation with monitoring
Finally, after the model has been validated, it must be put into production with a robust monitoring system.
Tools like Vertex AI Pipelines help maintain traceability, measure performance, and identify errors or deviations.
Continuous monitoring ensures that the model remains useful and ethical over time.
For teams looking to prototype without code, check out our content on... How to create a SaaS with AI and NoCode.
Multimodal Learning and Embeddings

The ethics behind multimodal AI involve concepts such as self-supervised multimodal learning, where models learn from large volumes of unlabeled data, aligning their representations internally.
This results in multimodal embeddings, which are numerical vectors that represent content from different sources in a shared space.
These embeddings are crucial for tasks such as cross-modal indexing, where a text search can return relevant images, or vice versa.
This is transforming sectors such as e-commerce, education, medicine, and entertainment.

Future and Trends of Multimodal AI
The future of multimodal AI points to the emergence of AGI (Artificial General Intelligence), an AI capable of operating with general knowledge in multiple contexts.
The use of sensors in smart devices, such as LiDARs in autonomous vehicles, combined with foundational multimodal models, is bringing this reality closer.
Furthermore, the trend is for these technologies to become more accessible and integrated into daily life, such as in customer support, preventative healthcare, and the creation of automated content.
Entrepreneurs, developers, and professionals who master these tools will be one step ahead in the new era of AI.
If you want to learn how to apply these technologies to your project or business, explore our... AI and NoCode training for creating SaaS..
Learn how to take advantage of Multimodal AI right now.
Multimodal AI is not just a theoretical trend: it's an ongoing revolution that is already shaping the future of applied artificial intelligence.
With its ability to integrate text, images, audio, and other data in real time, this technology is redefining what is possible in terms of automation, human-machine interaction, and data analysis.
Investing time in understanding the fundamentals, tools, and applications of multimodal AI is an essential strategy for anyone who wants to remain relevant in a market that is increasingly driven by data and rich digital experiences.
To delve even deeper, see the article about Context Engineering: Fundamentals, Practice, and the Future of Cognitive AI And get ready for what's coming next.