I'm going to show you, in practice, how to move beyond generic customer service. We're going to build a system. multi-agent with AIs experts. Each agent responds based on reliable data and updated.
Table of Contents
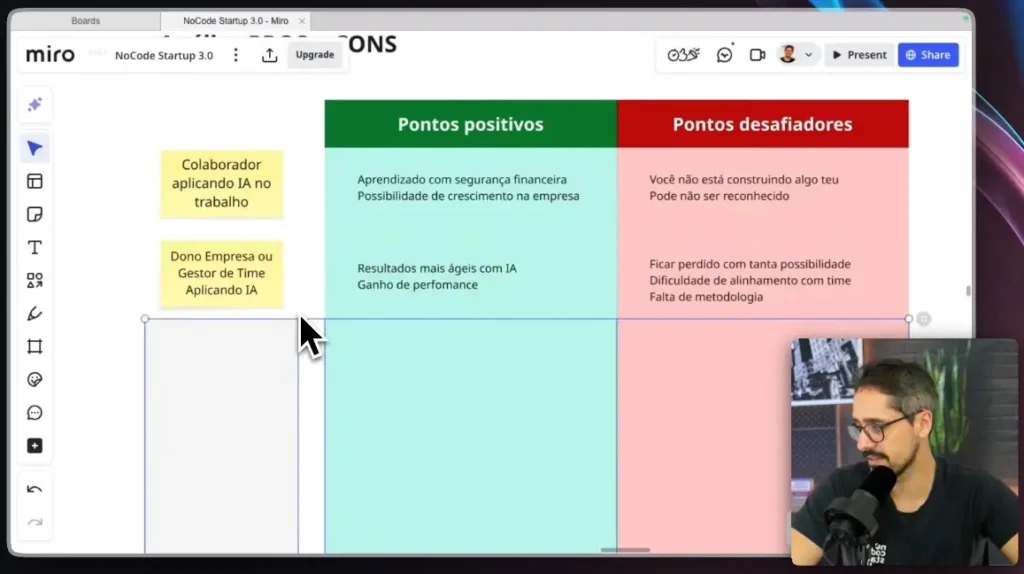
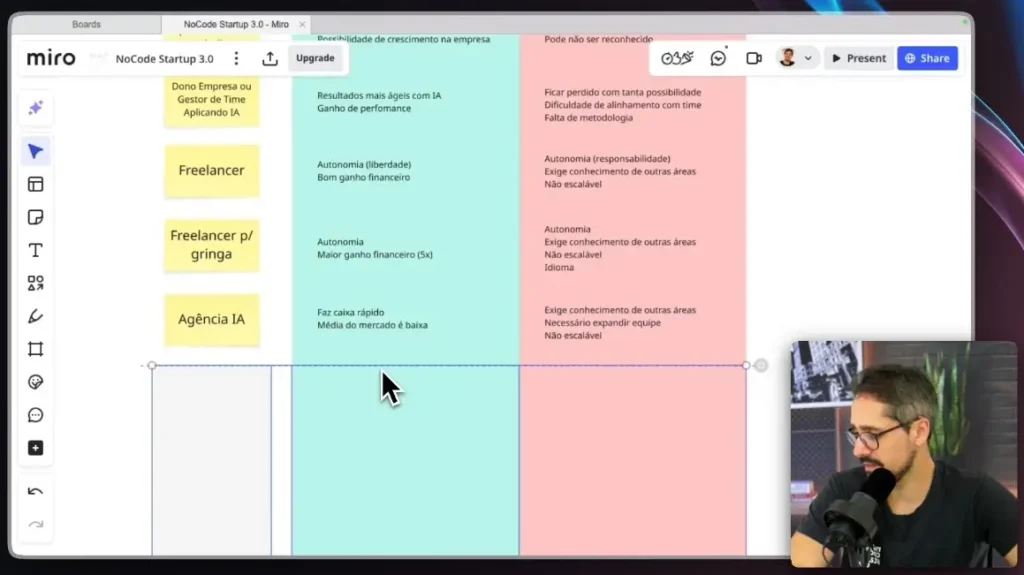
The problem of repetitive customer service in companies.
Have you ever wasted hours answering the same questions? Or seen a generic AI make mistakes on simple technical questions? This is the bottleneck that undermines satisfaction and scalability.
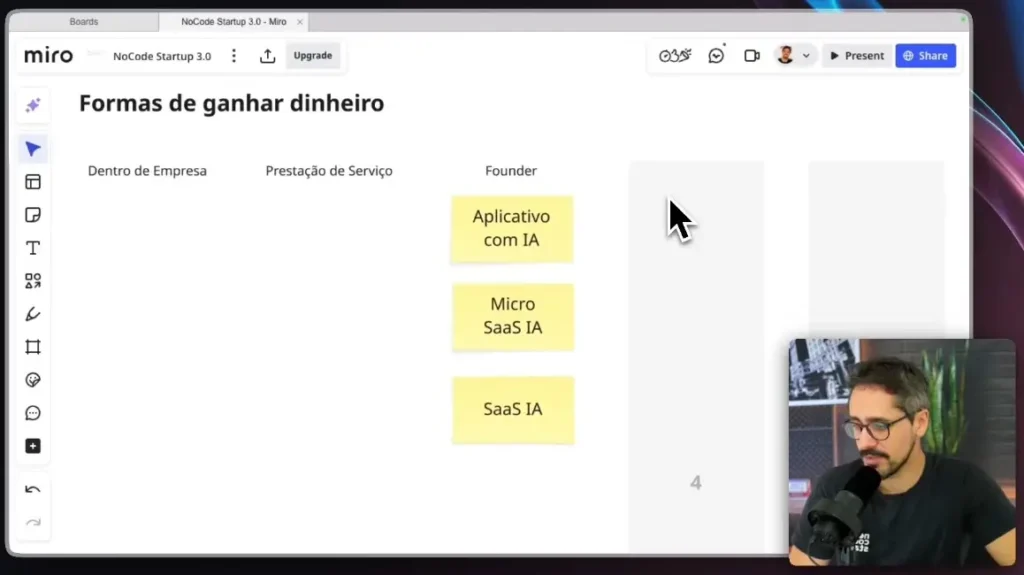
What works is specialization + context. Instead of an agent that does everything, we created... several specialists. Each one solves a part of the process with precision.
Architecture of an Agent project
Layered view
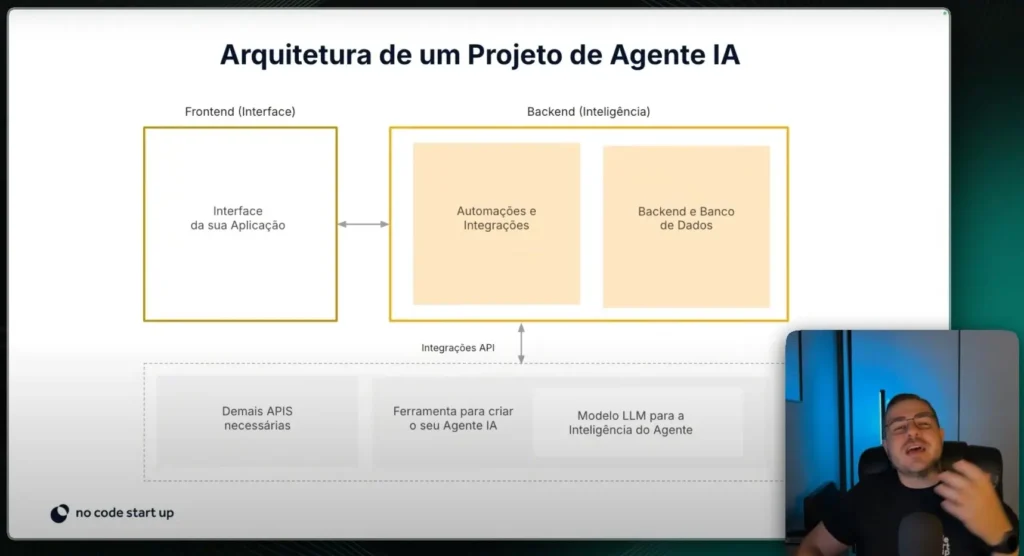
Front-end: User chat (n8n Chat Trigger or web/chat). Orchestration: flows in n8n coordinating agents and tools. Knowledge: vector bases in Supabase (Postgres + pgvector).
Main components
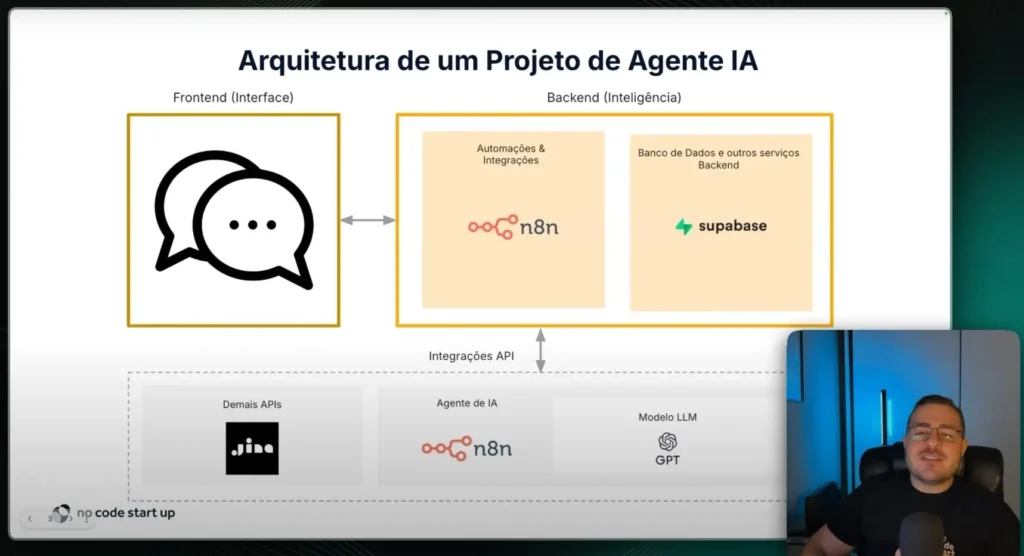
Orchestrating Agent: He receives the question and decides which path to take. Specialist Agents: n8n, Lovable and FlutterFlow. RAG: Semantic search in the official documentation of each tool.
Summary flow
User asks a question → Orchestrator classifies it → Expert consults RAG. Expert generates an answer with sources → Orchestrator delivers it in the chat. Logs and metrics are saved for continuous improvement.
The role of the Orchestrating Agent in orchestrating the flows.
The orchestrator is the conductor of the system. It classifies the intention, asks for clarifications when necessary. Only then does it delegate to the correct specialist.
He applies quality policies. Formats responses, includes citations/links, and sets limits. If context is lacking, prompts the user for minimal information.
Also manages fallbacks. If one expert fails, another is tried, or reliable guidance is provided. This ensures stability even in error scenarios.
Practical demonstration: experts responding in real time.
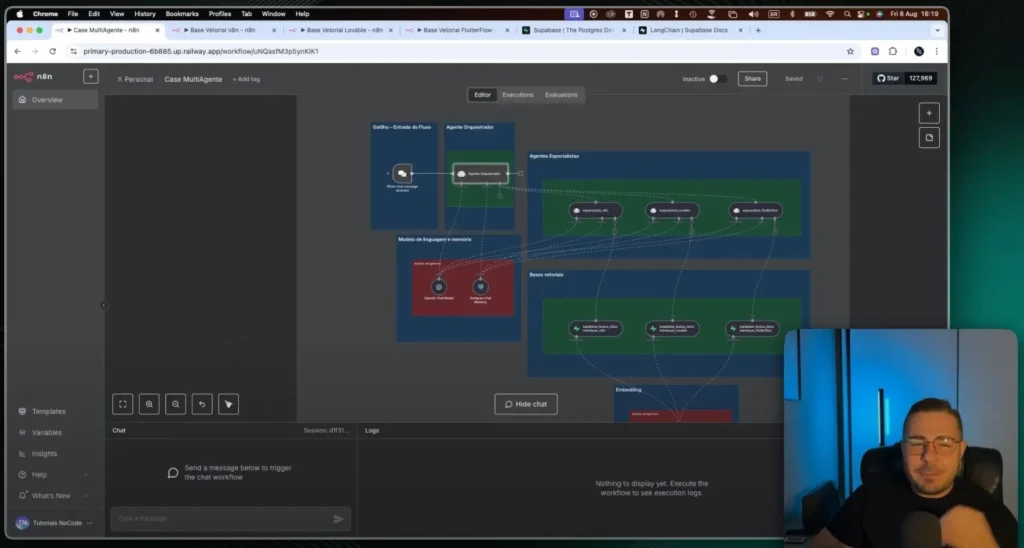
When the user asks about n8n, The orchestrator routes the data. The n8n expert consults the vector database for that document. The response comes structured with steps and best practices.
If the question is about Lovable or FlutterFlow, The same logic applies. Each specialist reads only their own isolated knowledge base. This avoids confusion and improves accuracy.
Messages and decisions are recorded. This allows us to measure response time, accuracy, and costs. And we optimize prompts and thresholds with real data.
Knowledge base preparation
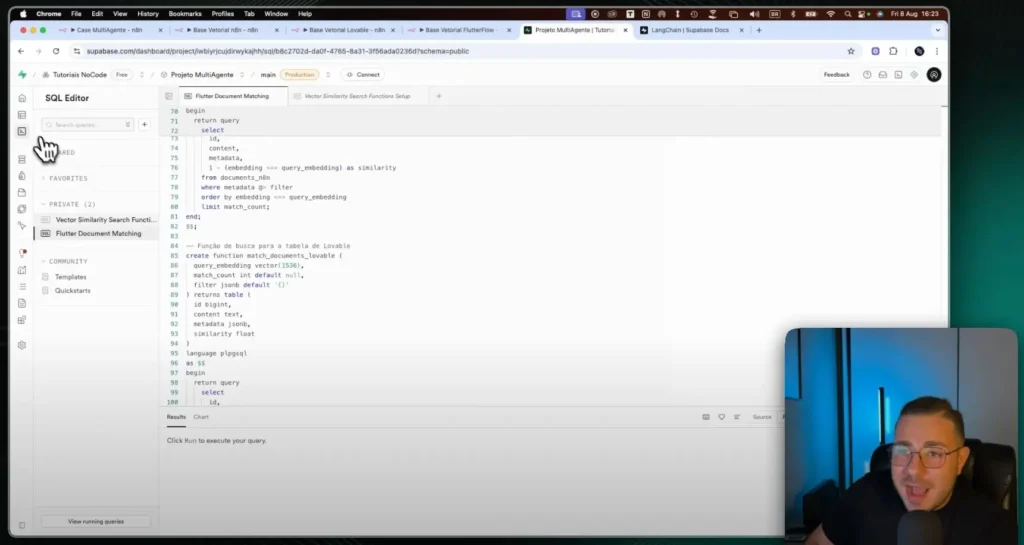
Intake pipeline
- Collect: use Jina Reader to extract clean pages.
- Processing: Cleaning, chunking, and metadata (source/URL).
- Embeddings: generation with OpenAI (text-embedding-3).
- Indexing: insertion into Supabase with pgvector.
- Observability: Scheduled jobs and versioning.
Good practices
Separate a table by tool. Store title, URL, excerpt, embedding, and date. Use the version to see what has changed and when.
Meet Jina AI
THE Jina AI It offers tools for data pipelines. In the project I use the Jina Reader to extract clean content. Works via URL shortcut or by API with key.
Advantages: speed, simplicity, and zero initial cost. Great for POCs and to keep the documentation always up-to-date. Integrates well with n8n and vector databases.
Examples of real questions and answers from the system.
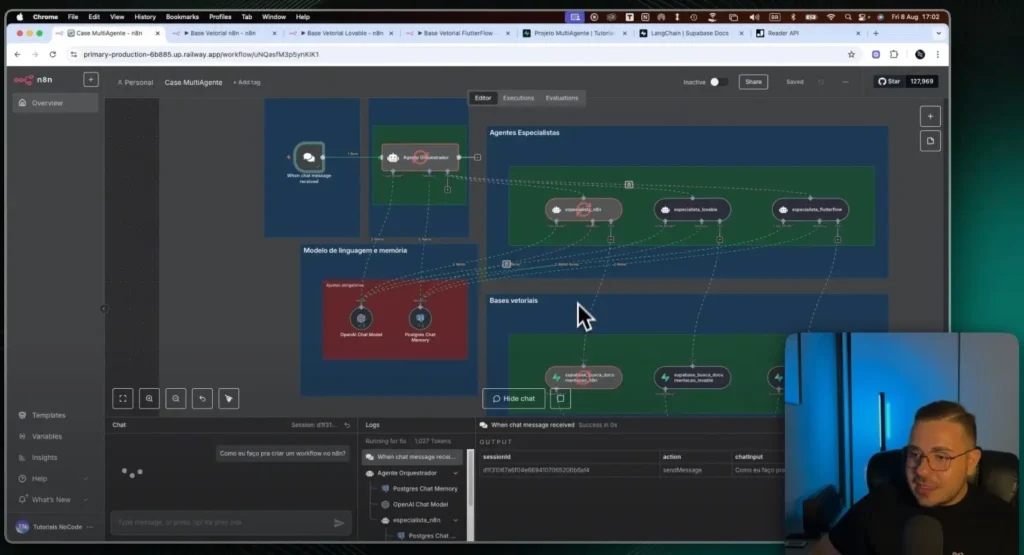
Question (n8n): How do I create a workflow from scratch? Response: Create workflows, add triggers, chain nodes. Manually test, save, and activate. Suggest templates.
Question (Loveable): How do I generate a quick dashboard? Response: Create project, define schema, import data. Generate automatic UI and customize components.
Question (FlutterFlow): How to consume a REST API? Response: Configure endpoints, map fields and states. Test requests and handle errors in the navigation flow.
Test with ambiguous questions and system limitations.
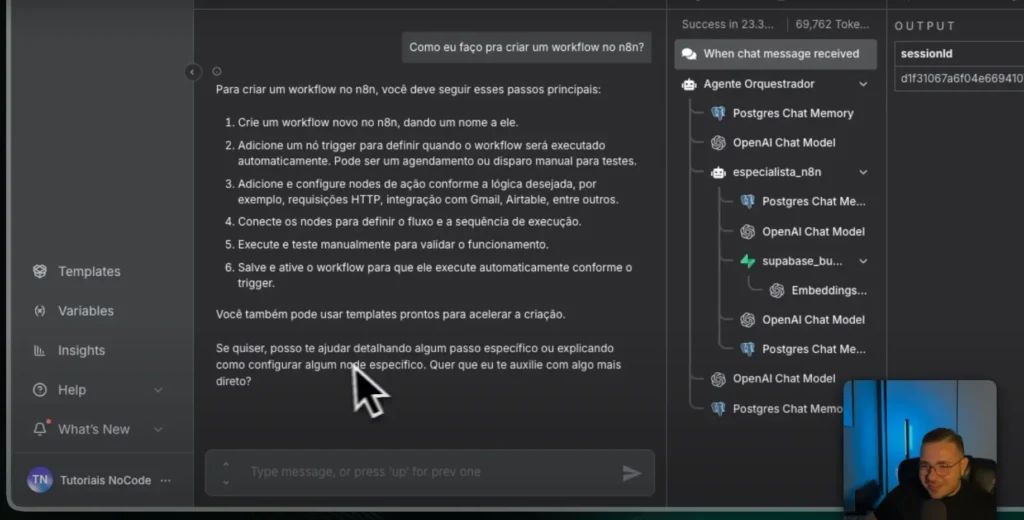
When the question is generic (e.g., "How to automate?"), the orchestrator requests the target tool. This avoids vague answers and reduces costs.
If the user asks for something out of scope (ex.: ZapierThe system responds with transparency and alternatives. It's better to be clear than to "invent" answers.
Limitations exist: outdated databases and poor prompts. We mitigate this with monitoring, re-ingestion, and prompt revisions. And satisfaction metrics to close the loop.
Reference stack
Models: GPT-5 Thinking (orchestration); GPT-5 Mini for general use. Embeddings: text‑embedding‑3; optional local Llama/Mistral. Orchestration: n8n (AI Agents + HTTP + Schedulers).
Knowledge: Supabase + pgvector; logging in Postgres. Extraction: Jina Reader (shortcut/API) with Markdown normalization. Messaging: Web/App chat; optional WhatsApp/Slack.
Quality: Source validation, minimum score, and fallback. Observability: Metrics by agent, cost, latency, and accuracy. Security: RBAC, PII masking, and audit trail.
Multi-agent systems solve what generic AIs can't. The right architecture, specialization, and data make all the difference. With this blueprint, you can start your pilot today.
If you want, I can generate them. n8n workflows Initial steps. I've included prompts, table schemas, and ingestion jobs. This allows you to test quickly and reliably measure ROI.
Additional Content: