The adoption of AI agents has ceased to be a futuristic differentiator and has become a real strategic lever for companies seeking competitiveness, operational efficiency, and scalable innovation.
These agents, which go far beyond simple virtual assistants, are redesigning processes, optimizing workflows, and opening new horizons for business models based on artificial intelligence.
By understanding the fundamentals, methodologies, and applications of these autonomous systems, it is possible to reduce technological and cultural barriers—a critical condition for the adoption of AI agents in any organization.

What are AI agents and why are they different from simple algorithms?
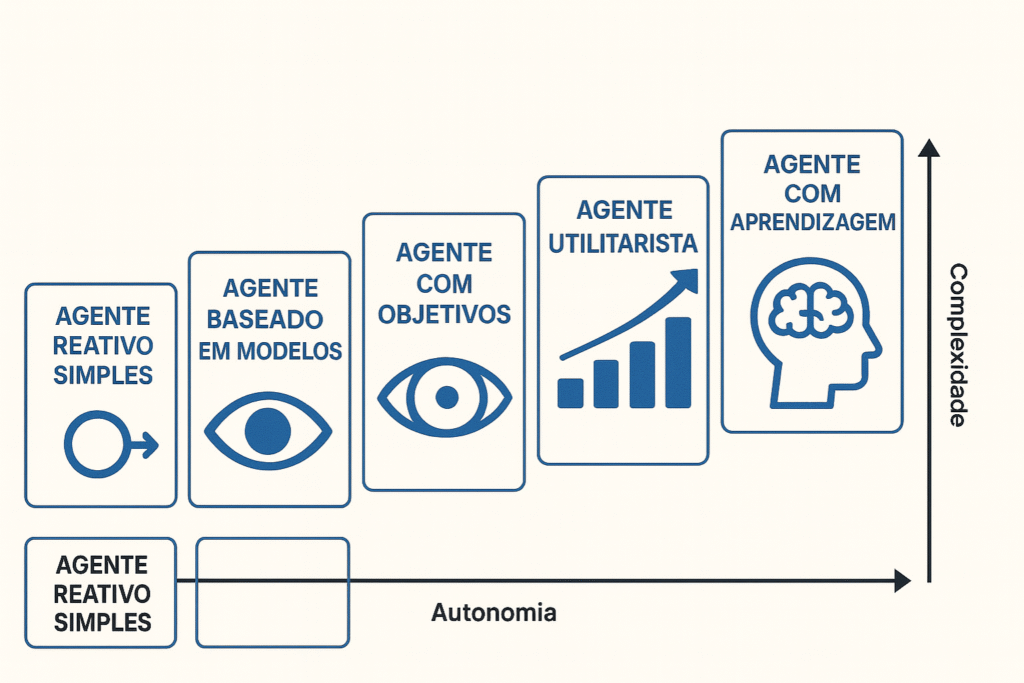
AI agents are computer systems capable of making autonomous decisions based on defined objectives and interactions with the environment.
They operate with agentic intelligence, meaning they have the ability to observe, plan, act, learn, and adapt as they accumulate experience.
Unlike traditional AI systems, which perform static or rule-based tasks, modern agents use language models such as GPT-4 or Claude to interact with dynamic data.
These systems are able to integrate legacy systems and generate concrete actions based on flexible rules, adapting to different contexts and continuously learning from each interaction.
This distinction is essential, as detailed in Astera and Oracle, by exploring the true potential of these systems in corporate environments.
How does the adoption of AI agents work in practice?
The journey to adopting AI agents can vary, but it generally involves four stages: identifying opportunities, prototyping, operational integration, and scalability.
During the identification phase, it is common to use frameworks such as... “"AI Readiness Model"” Deloitte's approach to assessing the company's digital maturity, as explored in this article.
Prototyping involves the use of platforms such as Make (Integromat) or N8N to create agents that automate repetitive tasks and communicate between applications.
Integration is the moment to consolidate these automations within the company's real workflows, respecting issues such as privacy, security, and performance.
Ultimately, scalability depends on continuous monitoring, refinement, and the adoption of good governance practices.

Main tools and technologies used
Modern AI agents rely on a powerful combination of LLMs (Large Language Models), API integrations, and no-code/low-code frameworks.
Among the highlights are:
- GPT-4 and ClaudeCognitive engines for decision-making.
- LangChain and AutoGen: for creating agentic pipelines.
- DifyA platform for building conversational agents and internal assistants. → Dify Course
- Xano and AppGyverBack-end and no-code logic. → Xano Course
- Bubble and FlutterFlow: creation of interfaces connected to agents. → FlutterFlow Course
These tools have been explored in training programs such as... Training for Agent and Automation Managers in AI from No Code Start Up, which prepares professionals to lead the implementation of these solutions.

Use cases that prove the value of AI agents.
The application of AI agents is transforming operations across various sectors with measurable and scalable results.
Below are some of the most relevant case studies, demonstrating how these solutions are being implemented in practice with a direct impact on business indicators.
Customer Service: Drastic reduction in response time
The company highlighted by CIO It managed to reduce response time in its call center by 90% by integrating trained conversational agents with CRM data and call scripts.
This efficiency gain generated significant operational savings and improved the NPS.
Internal Automation: Efficiency in administrative functions
Second Google Cloud search, 49% of Brazilian companies have already implemented AI agents to automate tasks such as data collection, email classification, and management reporting.
These agents operate invisibly, optimizing repetitive tasks that previously required several hours per week.
Corporate IT: Reducing the operational burden
In a case study published by Botpress, An IT team managed to reduce the time spent on administrative activities and internal support by 60% using agents who monitor systems, categorize tickets, and proactively respond to first-level requests.
Logistics and Supply Chain: Intelligent forecasting and automation
In the supply chain, autonomous agents were used by a retail network to predict seasonality and optimize replenishment orders, according to a study by Oracle.
Based on historical data and external variables, the system was able to reduce stockouts and logistical surpluses.

Barriers and challenges in the adoption of AI agents.
Despite the obvious benefits, many companies face cultural resistance, difficulties integrating with legacy systems, and a lack of internal knowledge.
That's why programs like NoCode AI Training SaaS They are fundamental to accelerating the development of technical leaders with a product-oriented mindset based on AI.
It is also critical to address issues such as security, privacy, and the ethical governance of these agents.
Organizations such as Stanford HAI They are already monitoring the impact of these technologies on a global scale.
The future of AI agent adoption
In the coming years, the trend is for autonomous agents to become key players in enterprise platforms, with the ability to proactively execute complete operations.
Reports such as the one from Precedence Research They project annual growth exceeding 35% in the agent market until 2034.
Organizations that want not only to keep up with this evolution, but to lead it, need to adopt an experimental stance, invest in training, and establish clear implementation pipelines.